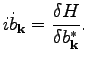Next: Near-identity transformation
Up: Canonical Hamiltonians for waves
Previous: Bogolyubov transformation of the
Canonicity conditions for near-identity transformation
Here, we obtain the canonicity conditions for the coefficients of the near-identity transformation (84).
For the canonicity up to
 order, we use the equation of motion in the Hamiltonian form.
order, we use the equation of motion in the Hamiltonian form.
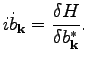 |
|
|
(99) |
In this Appendix for simplicity of notation, we skip writing
 in the subscript of the dynamical variables.
Using Eq. (84), we obtain
in the subscript of the dynamical variables.
Using Eq. (84), we obtain
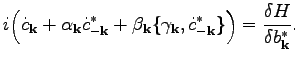 |
|
|
(100) |
Since we are neglecting terms of the order higher than
 , we can use the following approximation
, we can use the following approximation
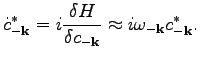 |
|
|
(101) |
Combining Eqs. (110) and (111), we obtain
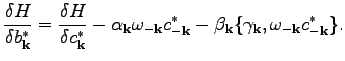 |
|
|
(102) |
Further, we have the chain rule in the form
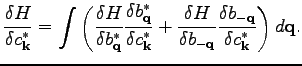 |
|
|
(103) |
Using Eq. (84), we find
where the subscript of the Poisson bracket indicates the differentiation with respect to
 .
Therefore, Eq. (113) becomes
.
Therefore, Eq. (113) becomes
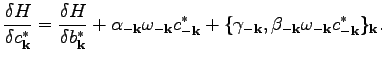 |
|
|
(104) |
Combining Eqs. (112) and (114), we find
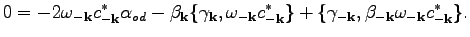 |
|
|
(105) |
Finally, we obtain the canonicity conditions given in Eq. (85).



Next: Near-identity transformation
Up: Canonical Hamiltonians for waves
Previous: Bogolyubov transformation of the
Dr Yuri V Lvov
2008-07-08