


Next: The Dyson-Wyld equations
Up: Diagrammatic Approach to Acoustic
Previous: Diagrammatic Approach to Acoustic
Let us define the ``bare'' Green's function of Eq. (2.24) as
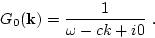 |
(63) |
One may see from (2.24) that this function describes the response
of the system of noninteracting acoustic waves on some external force.
We added in the denominator the term  by requirement of
causality. We remark that causality (the arrow of time) is introduces
in the perturbation approach by the limit
by requirement of
causality. We remark that causality (the arrow of time) is introduces
in the perturbation approach by the limit  and the fact
that
and the fact
that  appears in (1.7). Next we introduce the
``dressed'' Green-function which is the response of interacting wave
systems on this force:
appears in (1.7). Next we introduce the
``dressed'' Green-function which is the response of interacting wave
systems on this force:
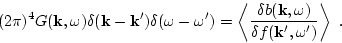 |
(64) |
We will be interested also in the double correlation function
 of the acoustic field
of the acoustic field 
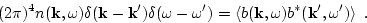 |
(65) |
The simultaneous double correlator of the acoustic field  is determined by
is determined by
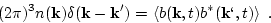 |
(66) |
This is related to the different-time correlators in the  representation
representation
 as follows:
as follows:
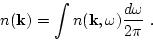 |
(67) |
The Green's and correlation functions together with the bare vertex
 (2.20) are the basic objects of
diagrammatic perturbation approach which we are going to use (see Fig
1a).
(2.20) are the basic objects of
diagrammatic perturbation approach which we are going to use (see Fig
1a).
Figure 1:
Panel (a): Basic objects of diagrammatic pertubation approach.
Panel (b): First terms in the expansion of mass operator
 .
.
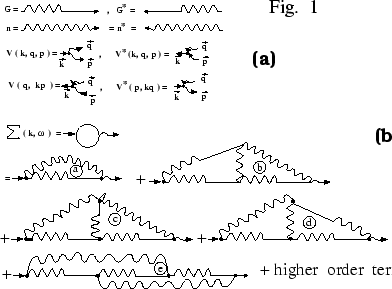 |
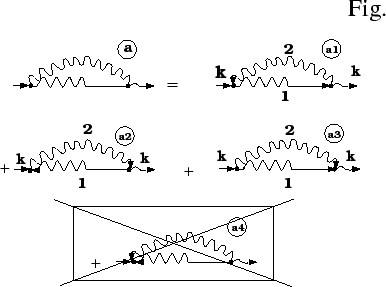
Figure 2:
Diagrams (a) from Fig.1 with specified directions of arrows.
 |



Next: The Dyson-Wyld equations
Up: Diagrammatic Approach to Acoustic
Previous: Diagrammatic Approach to Acoustic
Dr Yuri V Lvov
2007-01-17
![]() (2.20) are the basic objects of
diagrammatic perturbation approach which we are going to use (see Fig
1a).
(2.20) are the basic objects of
diagrammatic perturbation approach which we are going to use (see Fig
1a).
